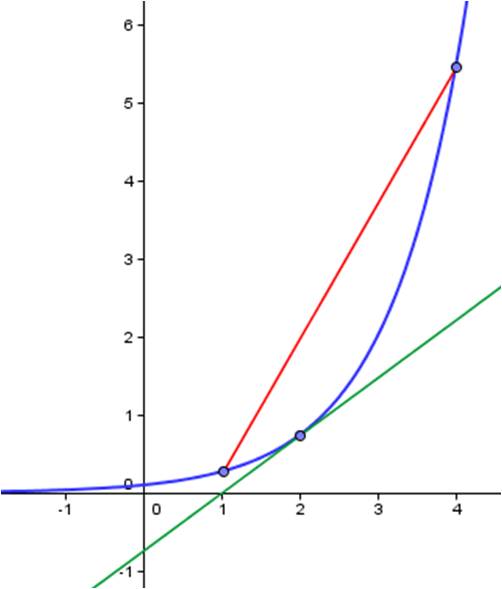
The average rate of change on an interval is the slope of the secant line on that interval. The instantaneous rate of change at a point is the slope of the tangent line.
Example: In the picture below, the blue curve is f(x). The red segment is the secant line between x = 1 and x = 4. The slope of this line is the average rate of change between 1 and 4. The green line is the tangent line to the curve at x = 2. Its slope is the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x = 2.
To find the average rate of change between 1 and 4, determine the coordinates of the endpoints of the red secant line and calculate the slope. To find the instantaneous rate of change at x = 2, calculate f’(2).